PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
UN NO.
TOXICITY
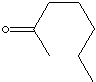
SMILES
CLASSIFICATION
Solvent, Ketone, Flavors and Fragrances
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
47 C
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/
Major Uses:
Industrial solvent; solvent for synthetic resin
finishes; fragrance ingredient in creams, lotions, perfumes, soaps &
detergents; flavor ingredient in foods; inert reaction
medium
Solvent for nitrocellulose
lacquers.
Blue cheese
flavor
In perfumery as constituent
of artificial carnation oils; as industrial solvent
Methyl n-amyl ketone is used
as a solvent in metal roll coatings and in synthetic resin finishes and
lacquers, as a flavoring agent, and in perfumes.
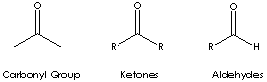
Local: Ketone is a class of chemical compounds contain the carbonyl group in which the carbon atom is covalently bonded to an oxygen atom.
Carbonyl groups are:
- Aldehydes (X and Y = H; X = H, Y = alkyl or aryl)
- Ketones (X and Y = alkyl or aryl)
- Carboxylic acids (X = OH, Y = H, alkyl, or aryl)
- Esters (X = O-alkyl or aryl; Y = H, alkyl, or aryl)
- Amides (X = NH, N-alkyl, or N-aryl; Y = H, alkyl, or aryl)
- Acid halides
- Acid anhydrides
- Lactones
- Lactams
Ketone has the general formula RCOR' where the groups R and R' may be the same or different, or incorporated into a ring (R and R' are alkyl, aryl, or heterocyclic radicals). The simplest example, R and R´ are methyl group, is acetone (also called 2-propanone, CH3COCH3) which is one of the most important ketones used in industry (low molecular weight ketones are general purpose solvents.) In the IUPAC system, the suffix -one is used to describe ketone with the numbering of the carbon atom at the end that gives the lower number. For example, CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH3 is named 3-hexanone because the whole chain contains six carbon atoms and the oxygen is connected to the third carbon from the lower number. There are aromatic ketones of which acetophenone and bezophenone are examples. Ketones can be made by the oxidation of secondary alcohols and the destructive distillation of certain salts of organic acids. In addition to as polar solvents, ketones are important intermediates in the syntheses of organic compounds such as alkoxides, hydroxyalkynes, imines, alcohols (primary, secondary as well as tertiary), acetals, thioacetals, phosphine oxides, geminal diols, hydrazones, organic sulfite and cyanohydrins. 2-Hexanone is used as a solvent and an intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and pesticides.
APPEARANCE
clear liquid
ASSAY
99.0% min
151 - 152 C
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF SOLVENT
Polarity
The most common solvent is water. Other common solvents which dissolve substances that are insoluble (or nearly insoluble) in water are acetone, alcohol, formic acid, acetic acid, formamide. BTX, carbon disulfide, diemthyl sulfoxide, carbon tetrachloride, chloroform, ether, tetrahydrofuran, furfural, hexane and turpentine. They may be classified as polar and non-polar. Polar solvents, like water, have molecules whose electric charges are unequally distributed, leaving one end of each molecule more positive than the other. Usually polar solvent has O-H bond of which water (HOH), (CH3OH) and acetic acid (CH3COOH) are examples. Propanol, butanol, formic acid, formamide are polar solvents. Dipolar solvents which contain a C-O solid bond without O-H bond are acetone [(CH3)2C=O], ethyl acetate (CH3COOCH2CH3), methyl ethyl ketone, acetonitrile, N,N-dimethylformamide and diemthyl sulfoxide. Nonpolar solvents, like carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), benzene (C6H6), and diethyl ether ( CH3CH2OCH2CH3), have molecules whose electric charges are equally distributed and are not miscible with water. Hexane, tetrahydrofuran and methylene chloride are non-polar solvents. Polar solvents are hydrophilic but non-polar solvents are lipophilic. Polar reactants will dissolve in polar solvents. Non-polar solvents dissolve non-polar compounds best. Oil and water don't mix but separate into two layers. There are three measures of the polarity as "dipole moment", "dielectric constant" and "miscibility with water". Though low dipole moments and small dielectric constants indicates non-polar solvents, sharp boundaries between polar and non-polar solvents are not available. The polarity reflects the balance between a polar component (OH) and a non-polar hydrocarbon component, existing in the same molecule. If hydrocarbon character increases relatively, the polarity decreases. On an operational basis, solvents that are miscible with water are polar.
Polar Protic and Dipolar Aprotic
Protic refers to a hydrogen atom attached to an electronegative atom. Protic solvents can donate an H+ (proton) since they contain dissociable H+, such as hydrogen attached to oxygen as in a hydroxyl group, nitrogen as in a amine group. Examples are water, methanol, ethanol, formic acid, hydrogen fluoride and ammonia. Aprotic solvents don't has O-H bond but a C=O bond typically. Examples are acetone [(CH3)2C=O] and ethyl acetate (CH3COOCH2CH3). Polar protic solvents are useful in SN1 reaction, while polar aprotic solvents are SN2 reaction.
|
|
|
|
|
Density (g/ml) |
|
Polar Protic |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
0.998 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.791 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.789 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.803 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.810 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.21 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.049 |
|
|
|
|
| 1.134 |
|
Polar Aprotic |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
0.786 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.886 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.805 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.894 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.786 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.944 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.092 |
|
Non-Polar |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
0.655 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.879 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.713 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.326 |
|
|
|
|
| 1.594 |
PRICE INFORMATION